Nombre del producto: Tubo de aleación de titanio, tubo de titanio sin costura, tubo de titanio Astm, tubo de titanio
Diámetro exterior: 6-2500mm, (3/8 "-100")
Espesor: 0,3-150mm,(Sch10-Xxs)
Longitud: 2000mm, 2500mm, 3000mm, 5800mm, 6000mm,12000mm, etc
Estándar: Astm/Asme B338, B337, B861,B862,Jis H4631 Jis H4630 Aisi,Jis, dinar, En
Superficie: Ba,2b,No.1,No.4,4k,Hl,8k
Material: Titanio Gr1, Gr2, Gr3, Gr5, Gr7, Gr9 Gr12
Certificación: Iso, Sgs,Bv
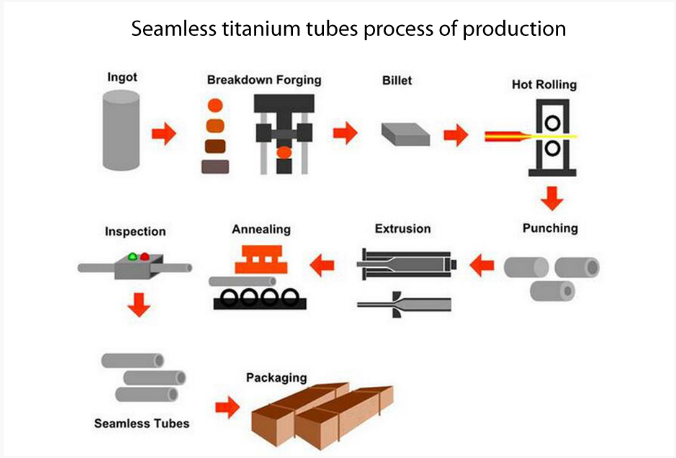
Técnica: Tubo sin costura dibujado en frío/tubo soldado
Borde: Borde de la raja del borde del molino
Aplicación: Es ampliamente utilizado en la industria eléctrica y de alta temperatura, dispositivos médicos, construcción, química, industria alimentaria, agricultura y componentes de barcos.
También se aplica al envasado de alimentos y bebidas, suministros de cocina, trenes, aviones, cintas transportadoras, vehículos, pernos, tuercas, resortes y malla de pantalla, etc.



 English
English Español
Español Français
Français بالعربية
بالعربية