-
- +86-186 7319 0580
- 0086186 7319 0580
- sales@super-steels.com
About Us

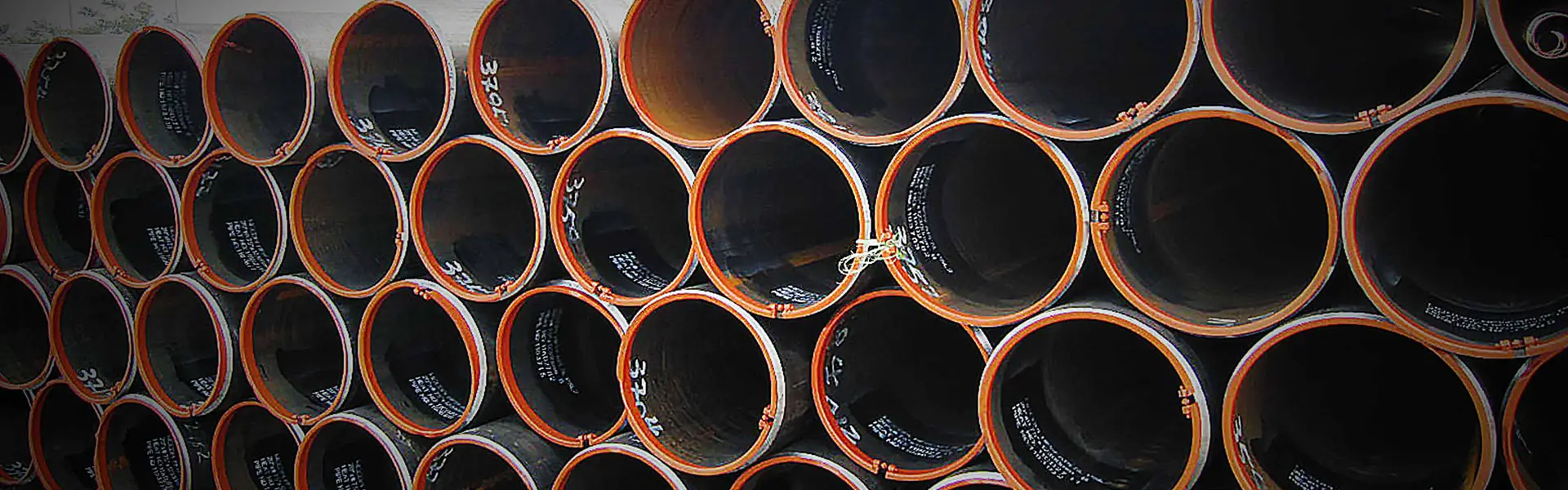
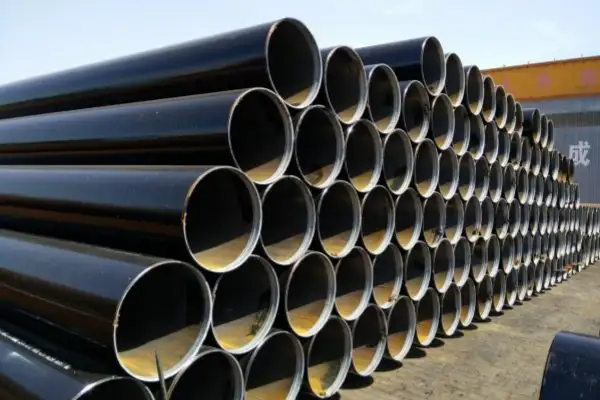
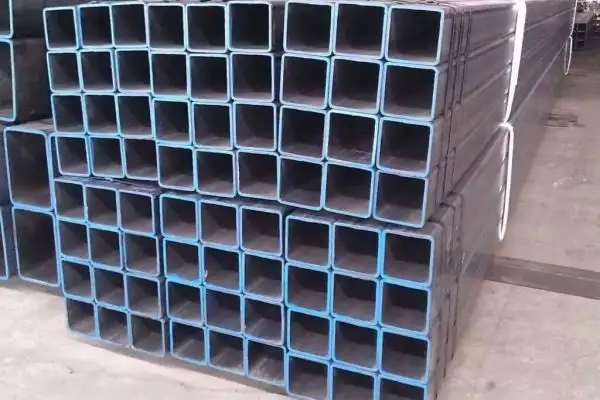
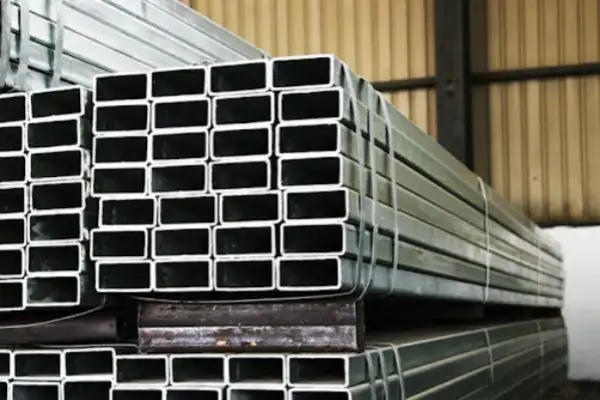
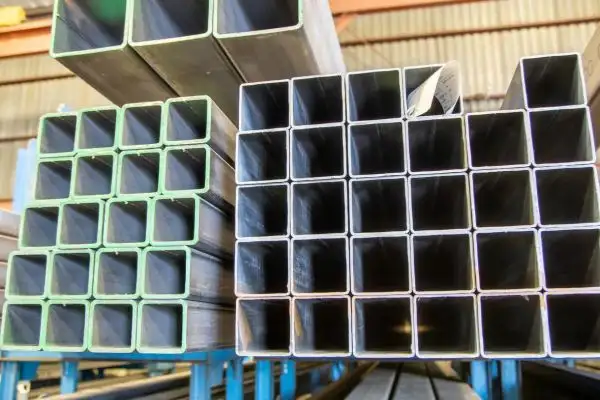
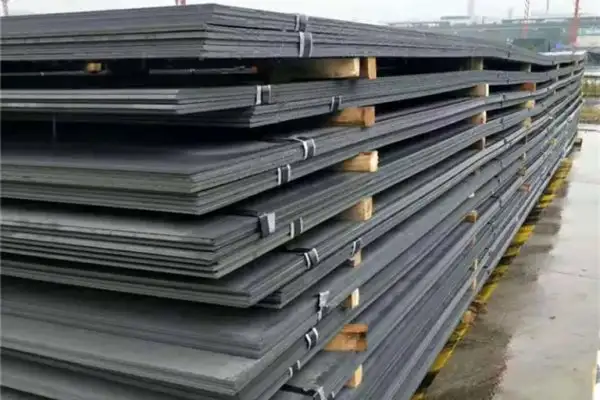
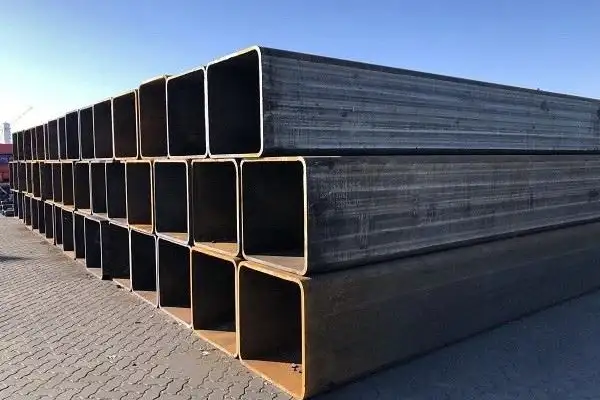
We Super Steel Manufacturing Co.,Ltd(SMC) are amongst the top manufacturers and suppliers for the seamless steel pipe, welded steel pipe, OCTG products and fittings from China. We have been manufacturing and supplying these products to the industry since 1993, and received repeat orders and appreciation from our valued customers.


 English
English Español
Español Français
Français بالعربية
بالعربية